Tonsillitis means that your tonsils are inflamed or infected. Your tonsils are the large, fleshy glands at the back of your throat (one on each side). These glands make antibodies that help fight infection.
While tonsillitis is most often seen in children adults of any age can get it, too.
Tonsillitis can be caused by either bacteria or viruses. Some of them include:
- Streptococcus (strep) bacteria; these germs are the most common cause of tonsillitis
- Adenoviruses
- Epstein-Barr virus, which causes infectious mononucleosis
- Herpes simplex virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Measles virus
Tonsillitis caused by these germs is contagious, which means it is usually easily passed from one person to another.
Why Choose Cooper to Treat Tonsillitis
As ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists, Cooper’s team of otolaryngologists – head and neck surgeons have extensive training and experience in treating adults with tonsillitis both medically and surgically. Should surgery (tonsillectomy) be required, they use today’s most minimally invasive techniques for less pain and faster recovery.
Risk Factors for Tonsillitis in Adults
The major risk factors for tonsillitis in adults are:
- Still having your tonsils: While many older adults may have had their tonsils removed when they were children—when surgery was a more routine approach to dealing with tonsillitis—a growing number of adults born in the 70s and later still have their tonsils, putting them at risk for getting tonsillitis
- Living or working in close proximity to children: Parents, grandparents, teachers—anyone in frequent contact with children, in whom tonsillitis is most common—are at increased risk of getting tonsillitis themselves
- Age: The elderly are more susceptible to infection due to a weakened immune system
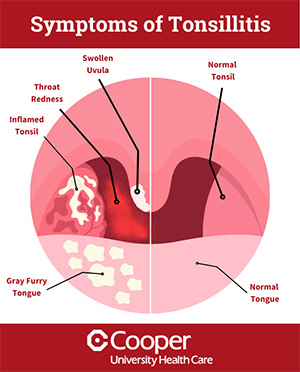
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
While each person may have slightly different symptoms, these are the most common symptoms of tonsillitis:
- Swollen, red tonsils; they also may look yellow, gray, or white, or have white spots/patches
- Blisters or painful sores on the throat
- Sore throat that happens suddenly
- Pain when swallowing or difficult to swallow
- Snoring
- Foul breath
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness
- Chills
- Fever
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck or jaw area
You may not have any symptoms but still have the strep bacteria, which you can spread to another person.
If tonsillitis is left untreated, a complication can develop called a peritonsillar abscess. This is an area around the tonsils that’s filled with bacteria, and it can cause these symptoms:
- Severe throat pain
- Muffled voice
- Drooling
- Difficulty opening mouth
How Tonsillitis in Adults Is Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and do a physical exam. To guide treatment, your provider may rub a sterile swab over the back of the throat and tonsils to get a sample of the secretions and perform:
- Rapid strep test: This test can detect strep bacteria in minutes
- Throat culture and sensitivity: The sample is cultured in a lab for the presence of bacteria; it helps the provider choose the best antibiotic to treat it, but can take 48 to 72 hours to get the results
How Tonsillitis Is Treated
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on what caused it, how severe it is, and your general health. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Tonsillitis caused by a virus is treated differently from tonsillitis caused by bacteria.Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is treated with antibiotic medicine. A mild case of tonsillitis doesn’t necessarily require treatment if a virus, such as a cold, causes it. Some cases of tonsillitis caused by a virus may be treated with antiviral medicine.
- Surgery: While surgery used to be a fairly common approach to dealing with tonsillitis, today, tonsillectomies are not performed unless the condition is chronic and recurring. If a person experiences tonsillitis seven times within a single year or 3 episodes per year for 3 consecutive years, a doctor would probably consider surgery. A tonsillectomy might also be recommended if the tonsils are causing issues such as sleep apnea difficulty breathing or swallowing, or a difficult-to-treat abscess
- Self care/home care: To make yourself comfortable and ease the discomfort of a sore throat, be sure to:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Rest
- Gargle with warm salt water several times a day
- Use throat lozenges
- Avoid smoke
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen
Make an Appointment with a Tonsillitis Expert at Cooper
To learn more about the services available for treating tonsillitis at Cooper or to request an appointment, please call 800.8.COOPER (800.826.6737).
